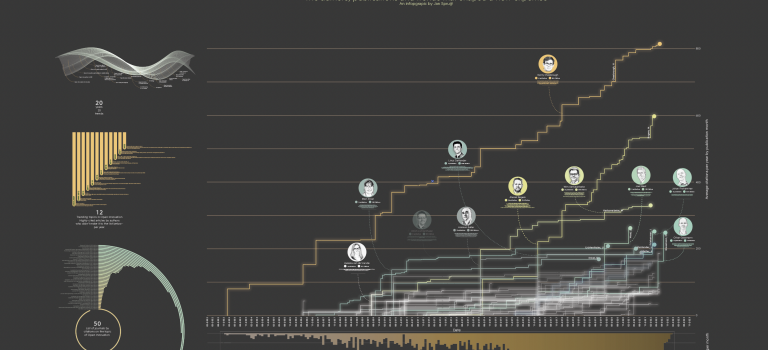
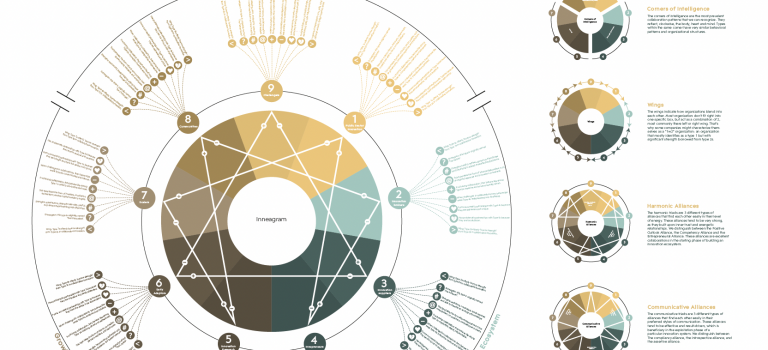
The story of this infographic began 16 years ago during a Summer School organized by the University of Cambridge. Not in the City of Perspiring Dreams itself, but on the mystical mountain Uludağ in Turkey, with 15 fellow students in a mountain hut more than 1 hour away from the nearest town with cellphone reception. On this mountain, led by Cambridge professor Jim Platts, we took an ESTIEM traineeship in transformative leadership. Without taking a deep dive into the material of the Summer School, one of the models that we started to work with was the Enneagram. Not only the power of the model itself, but also the history behind it, really intrigued me and so the story began.
Over the years, I’ve read much more about the Enneagram. Mostly used in (business) psychology, the framework is best described as an adaptive approach to recognize your own – and others’- behaviour in interactions with others. So it’s not, as many think, a framework for personality traits, like the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) or the Big-5 personality test. It perhaps holds the middle between these personality tests and the Rose of Leary, a theory of behavioral influence. The theory helps you to find your comfort-spot and from there on explains how your interactions with others happen and could be improved if you learn how to read it. It’s adaptable: it may change under different circumstances, under different preconditions and in different situations.
Read more →